Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (plural mycorrhizas , a.k.a. endomycorrhiza )
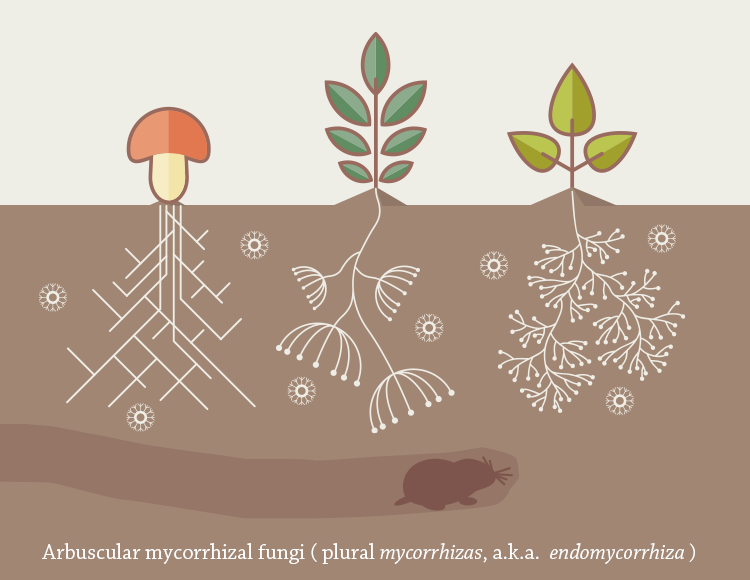
An arbuscular mycorrhiza (plural mycorrhizas, a.k.a. endomycorrhiza) is a type of mycorrhiza in which the symbiont fungus (AM fungi, or AMF) penetrates the cortical cells of the roots of a vascular plant forming arbuscules. (Not to be confused with ectomycorrhiza or ericoid mycorrhiza.)
Arbuscular Mycorrhizal (AM) fungi form symbiotic associations with most land plants and interact with a wide range of soil microorganisms. We have been developing the user-friendly web interface ‘Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi and Bacteria classification pipeline’ for rapid identification of fungi (including AM fungi) and bacteria from raw-sequence reads. The fungal reference database consists of the sequences of divergent D2 region of LSU including 524 AM fungal OTUs and 82,082 non-glomeromycotinan sequences obtained from 34 and 5 agricultural field across Japan and North America, respectively. The bacterial reference database consists of the sequences of 7,292 type strains and 300,706 sequences of V3-V4 regions of SSU. In the fungi mode of pipeline, users input fastq files of either paired-end (PE) or single-end reads generated by Illumina MiSeq. The pipeline connects PE reads and assigns to either AM fungal OTUs or non-glomeromycotinan fungal sequences through BLASTN searches against the database, and generates two OTU tables, ‘AM fungi assigned’ and ‘Other fungi assigned.’ Distinct characteristics of this pipeline is that each user can manage a private reference database, namely, user can construct their own database and add new OTUs/sequences found in 'unassigned reads' to the database. Since this pipeline provides the fixed OTU as an output, users can apply the obtained results for comparison between the independent experiments. This system would be applicable for the community analysis based different regions of ribosomal DNA and internal transcribed spacer regions.
The tremendous advances in research on mycorrhizal physiology and ecology over the past 40 years have led to a greater understanding of the multiple roles of AMF in the ecosystem. This knowledge is applicable to human endeavors of ecosystem management, ecosystem restoration, and agriculture.
What's new
- 2019.11.01
"Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi classification pipeline" website was renewed.
- 2023.07.24
Maximum likelihood tree of the 524 OTUs (Niwa et al., 2018) with the newly collected 174 LSU rDNA sequences obtained from culture collections (Delavaux et al., 2022) was constructed.
- 2024.2.24
The dataset including 684 OTUs for AM fungi has been released.
Reference data set
| release | date | sequence number | |
|---|---|---|---|
| AM fungi | other fungi | ||
| am00 | 2016/4/1 | 412 | 82229 |
| am01 | 2018/2/20 | 417 | 82082 |
| am02 | 2018/7/9 | 524 | 82082 |
| am03 | 2018/9/11 | 524 | 82082 |
| am04 | 2024/2/24 | 687 | 82082 |
(*) Detailed analytical methods are indicated in the figure.
| release | date | sequence number | |
|---|---|---|---|
| strain identified | unclassified | ||
| bct2016.0 | 2016/4/1 | 7293 | 300707 |
Primer set
| * Fungi (D2 region of LSU) |
| FLd3: 5'-GTGAAATTGTTGAAAGGGAAACG-3' |
| FLR2: 5'-GTCGTTTAAAGCCATTACGTC-3' |
| reference: Niwa R. et al, Sci. Rep. 2018, 8:7419. ( PMID: 29743529 ) |
This pipeline was made with the support by ACCEL project (JPMJAC1403) from Japan Science and Technology Agency.
